
Masao Akagi
When starting the national sabo project in 1926, the national government appointed Masao Akagi, who just came back from Europe, as the first director of Tateyama Mountain Area Sabo Office, Niigata Civil Engineering Branch Office, Ministry of Home Affairs (the current Tateyama Mountain Area Sabo Office, MLIT).
He thought it was important to plan a basic sabo facility at the exit of the Tateyama Caldera in order to prevent from a largre amount of sediment discharge, and decided to construct the Shiraiwa Sabo Dam with 63 m height. For its construction, he also decided to build the sabo work service train to efficiently transport a number of construction materials and workers because there was no sufficient roads to approach to the project site.

Tateyama Mountain Area Sabo Office in 1926
After in-depth field surveys, Akagi himself designed Shiraiwa Sabo Dam using concrete as a material to prevent debris flow.
Shiraiwa Sabo Dam and sabo facilities at the upstream segment planned by Masao Akagi
At that time, the only transport means were manpower or horsepower. To make it possible to construct Shiraiwa Sabo Dam and other sabo facilities in the Tateyama Caldera, a Erosion Control Works was constructed so that a large number of materials and equipment could be transported. This Service Trainis still active in sabo works in Tateyama.

Shiraiwa Sabo Dam during construction (1935)
What is sabo dam?
Sabo dam holds sediment from mountain slopes, riverbed and river bank to slow down the flow of the river, and prevents slope collapse and erosion of riverbed. It also plays a role to prevent a large volume of sediment from flushing into downstream area.
Effects of Sabo Dam
Prevention from Erosion in River Bed
Sabo dam that accumulates sediment plays a role to decrease the gradient in river bed and velocity of water flow, thus preventing it from being eroded.
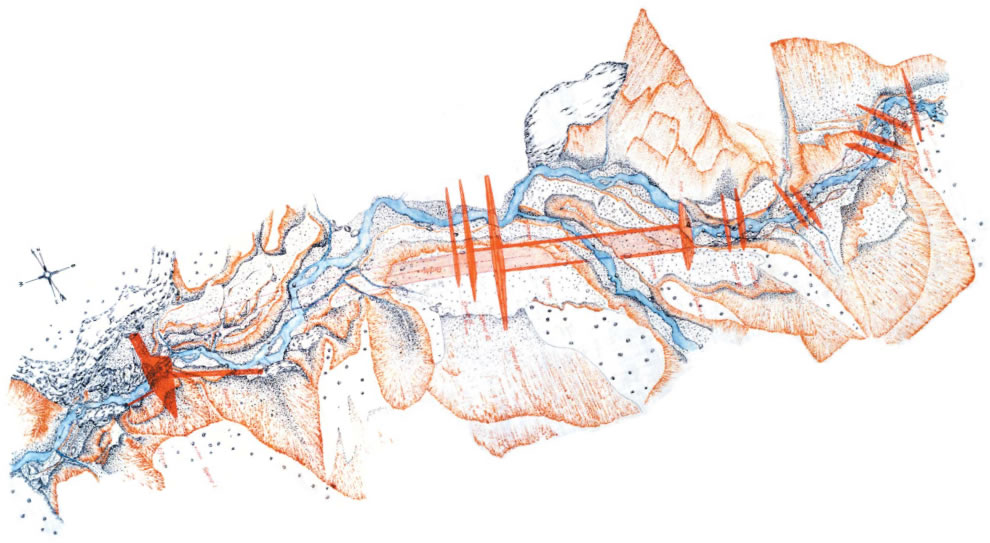
- Before construction
- After construction
- Decreases the river slope and change the quality of discharging sediment. (from big stones to small stones)
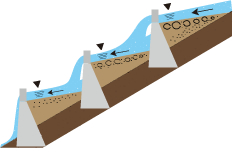
Prevention from Erosion and Collapse in slope of river bank
Sabo dam that accumulates sediment and raise the level of river bed help prevent erosion and slope failure on a river bank and mountain foot, because it is expected that accumulated sediment would play a role of stabilizing berm, and also expansion of river width and the decrease the velocity of water flow.
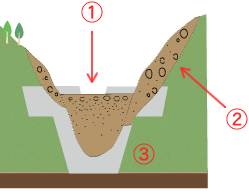
- ① River bed raised by the accumulating sediment.
② Hillside no longer collapses and becomes stabilized.
③ Widened river width slows down the water flow.
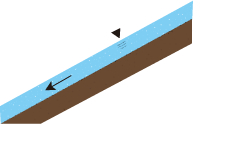
Mechanism of Imprermeable Sabo Dams Adjusting Sediment Flow
-
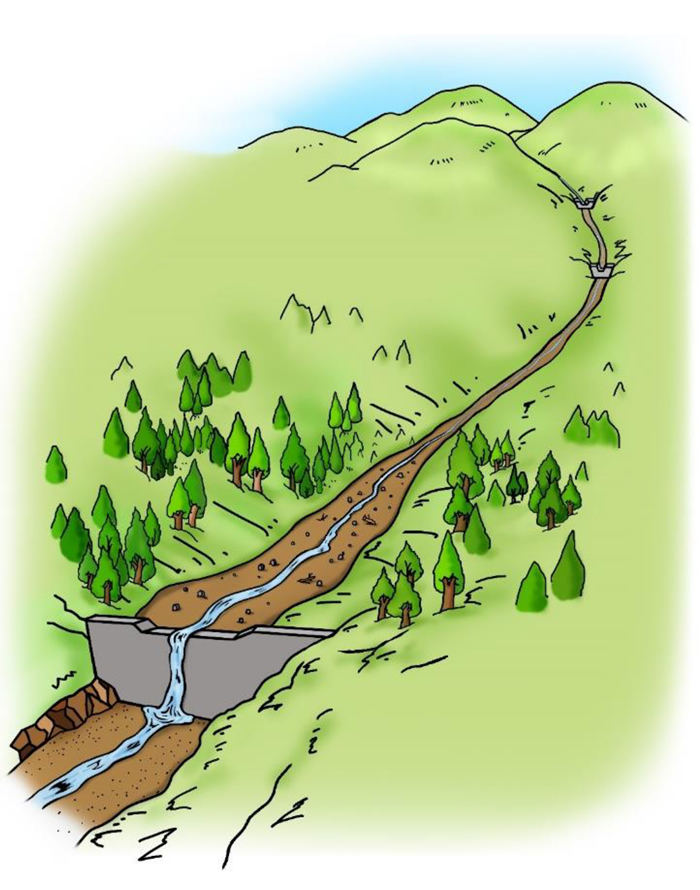
1) An impermeable sabo dam does not necessarily lose its effect even when it is fully filled with sediment. Sediment is deposited on the upstream side of the dam to make the river softer in gradient and wider in width and thus slow down the flow of water. -
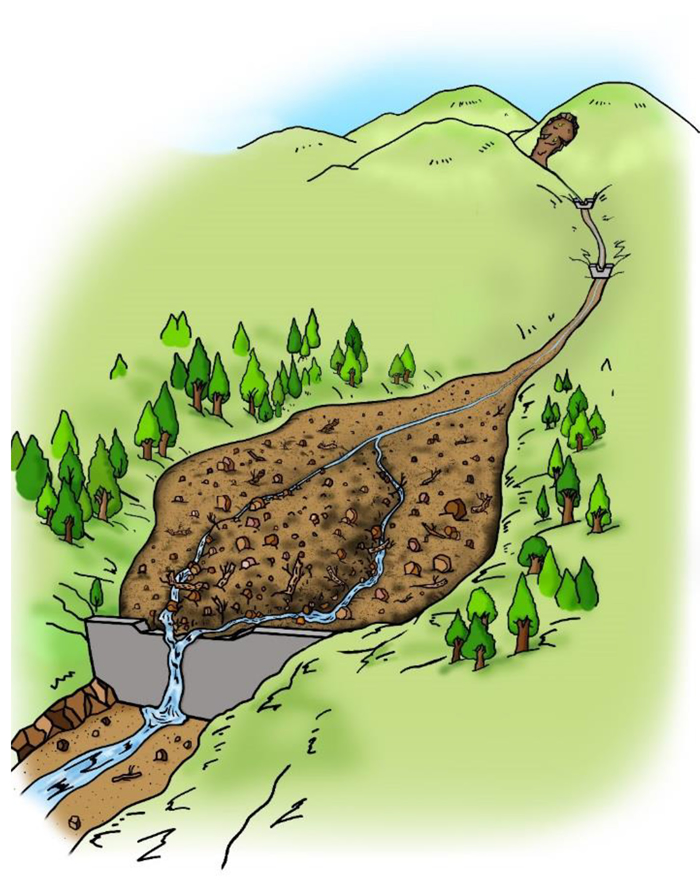

2) When a large amount of sediment flows down together with heavy rain, the water flow slows down on the upstream side of the dam, where the river gradient is gentle, and part of the sediment temporarily accumutates over the planned deposited sediments. -
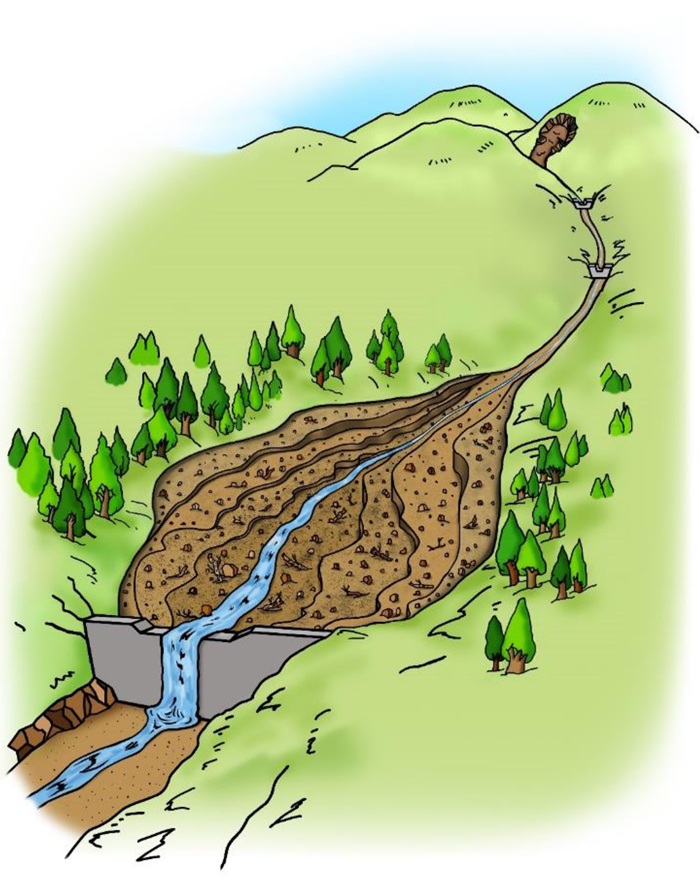

3) Overlying sediment then runs down little by little with the force of water every time rain falls. (Then, when heavy rain falls, the sediment again piles up as in (2) above.)
